
Global Leading Technology
Global Leading Technology
Experts and Scholars
International Research Platform and Expert Team
In November 2022, Infinitus upgraded its "Infinitus Scientific Advisory Board" to the "Infinitus Global Scientific Advisory Board." This new board includes multidisciplinary and multi-field experts from around the world, integrating traditional Chinese wellness wisdom with modern scientific methods to provide continuous professional consultation and technical support to Infinitus.
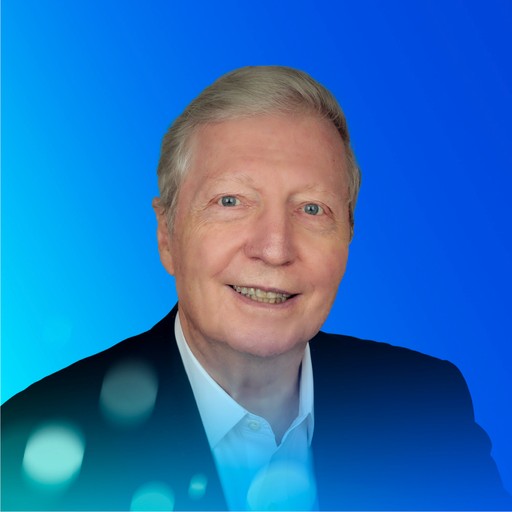

Jules A. Hoffman (French)
Nobel Prize laureate in Physiology or Medicine (2011)
Honorary Distinguished Research Director and Group Leader at the French National Center for Scientific Research (CNRS)
President of the French Academy of Sciences (2007-2008)
Hoffmann was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for his discoveries concerning the activation of innate immunity. He is renowned for his research on the genetic mechanisms and innate immune responses in insects, making him a globally recognized leader in the field of immunology.
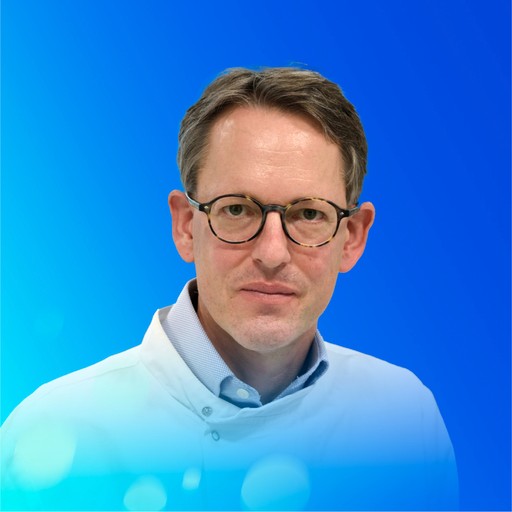

Clemens Kaminski (British)
Head of the Department of Chemical Engineering and Biotechnology at the University of Cambridge
Fellow of the Institute of Physics (2020)
Fellow of the Royal Society of Chemistry (2020)
Clemens Kaminski is an internationally renowned scientist in high-resolution imaging technology. He is a pioneer in integrating cutting-edge technologies, including modern molecular biology, high-resolution imaging, and deep learning technologies. His work is dedicated to the precise research and visualization of molecular and organelle mechanisms.
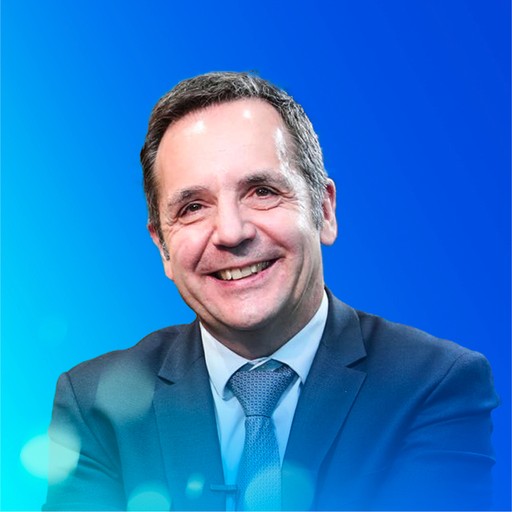

Jean-Luc IMLER (French)
Director of the Institute of Molecular and Cellular Biology at the French National Center for Scientific Research (CNRS)
Director of the laboratory Insect Models of Innate Immunity Research Unit at CNRS
Recipient of the CNRS Silver Medal (2020)
Jean-Luc Imler is a leading figure in the study of antiviral immunity in flies. He has long been engaged in research on the antiviral mechanisms of RNA interference (RNAi), inducible antiviral immunity, and the identification of host factors that regulate viral infections. His team was the first to reveal the RNA immunity mechanism against viral infections.
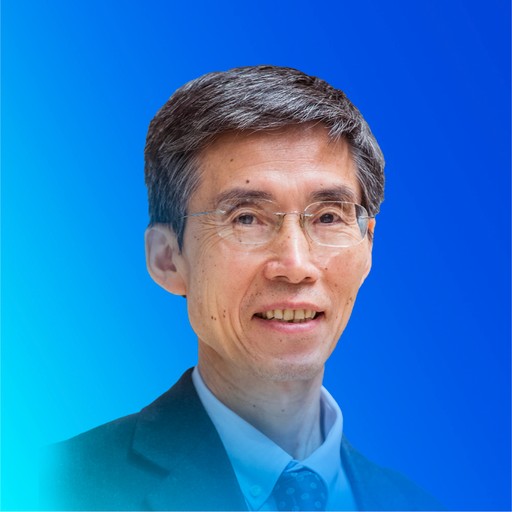

Zhang Yongmin (French)
Fellow of the French National Academy of Pharmacy (2012)
First-Class Research Director at the French National Center for Scientific Research (CNRS) (2013)
PhD Supervisor at the Sorbonne University (formerly Pierre and Marie Curie University)
Zhang Yongmin is a leading expert in the study of bioactive carbohydrates. He has made significant contributions to carbohydrate chemistry and polysaccharide research, excelling in the study of the dose-effect, spectrum-effect, and structure-effect relationships of complex polysaccharides, achieving international recognition.
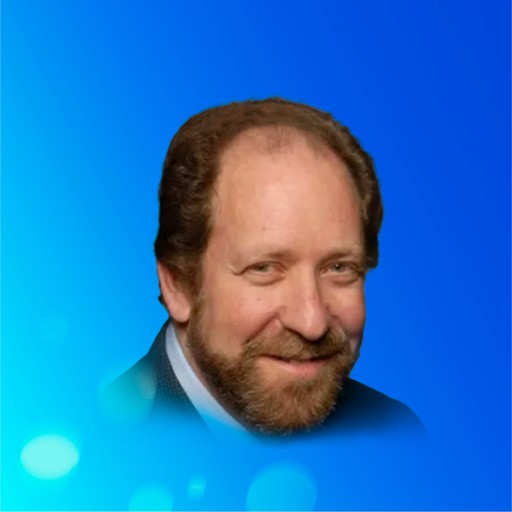

David M. Eisenberg (American)
Associate Professor at the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health
Founding Director of the Division for Research and Education in Complementary and Integrative Medical Therapies at Harvard Medical School (2000-2010)
Former Advisor to the National Institutes of Health (NIH), Food and Drug Administration (FDA), and the Federation of State Medical Boards
Eisenberg was the first American medical exchange student sent to China by the National Academy of Sciences in 1979. He specializes in the modern scientific validation of Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) and research on nutrition and disease prevention strategies, including lifestyle interventions. He offers unique insights into the contemporary medical interpretation of TCM wellness practices.
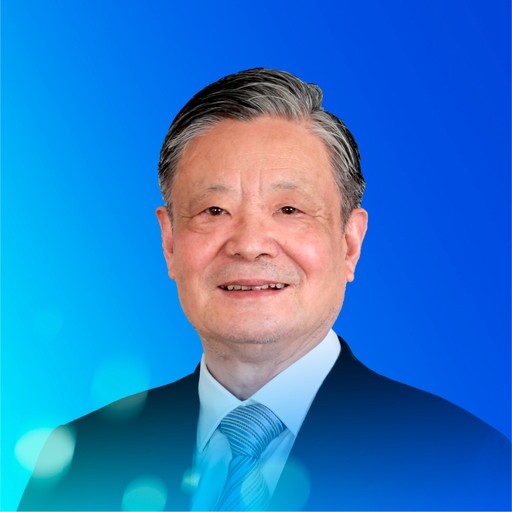

Wang Qi (Chinese)
Fellow of the Chinese Academy of Engineering (2019)
Certified National Chinese Medicine Master in the Second Guo Yi Da Shi selection
Lifetime Professor (First-Class Professor) at Beijing University of Chinese Medicine
Wang Qi discovered and defined nine types of Chinese body constitution. He initiated the Medical Health China Program of Nine Body Constitutions, then has developed and refined six major academic systems in Traditional Chinese Medicine: body constitution, male health, Zangxiang (phenomenon of organs), abdominal diagnosis, health medicine, and pre-disease medicine. His work has pioneered new areas of original thinking in Traditional Chinese Medicine.
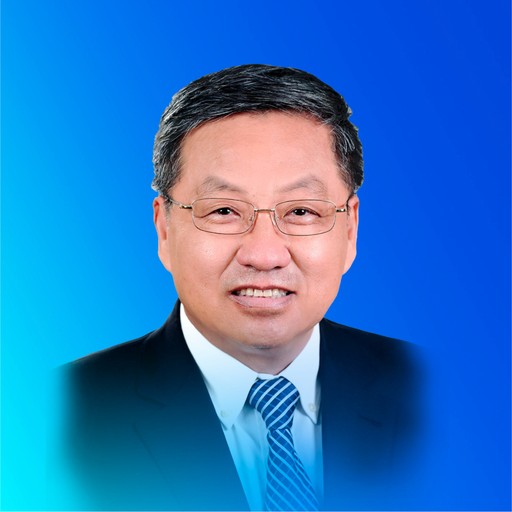

Wang Xinlu (Chinese)
Certified National Chinese Medicine Master in the Fourth Guo Yi Da Shi selection
Chief Health Science Popularization Expert at the Chinese Association of Chinese Medicine
Professor and PhD Supervisor at Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine
Wang Xinlu is a leading researcher in the study of blood stasis theory. Having long been engaged in theoretical research and clinical practice in Traditional Chinese Medicine, he has established a solid theoretical foundation, extensive professional knowledge, and sufficient clinical experience.
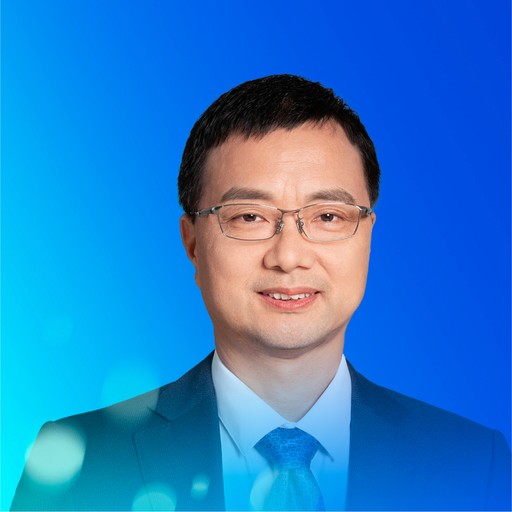

Du Zhiyun (Chinese)
Provincial Talent of the "Thousand-Hundred-Ten" Program in Guangdong Province
Foreign Member of the Russian Academy of Natural Sciences
Chairman of the Guangdong Cosmetics Association
Du Zhiyun specializes in utilizing natural medicines and Chinese herbs, with a focus on the dual-purpose application of food as medicine. Employing systems biology and experimental pharmacology, he dedicates his research to developing new drugs, medical translational applications, functional foods, and functional cosmetics. His work emphasizes fundamental research and the industrial transformation within the health industry.

Robert Kam Ming KO (Hong Kong, China)
Associate Head and Professor, Division of Life Science, Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST)
Associate Director of Center for Chinese Medicine Research and Development
Robert Kam Ming Ko specializes in the pharmacological mechanisms of Traditional Chinese Medicines and formulae. He is particularly skilled in researching the components of Schisandra Chinensis, an invigorating Chinese herb, and its mechanisms for free radical scavenging, antioxidation, and anti-aging.

Wang Xijun (Chinese)
Director of the Research Center for Classic Formulae of the Ministry of Education
Director of the Metabolomics Research Center for Chinese Herbal Formulae at the National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine
Advocate of the Key Discipline A+ in Traditional Chinese Medicine
Wang Xijun has dedicated himself to researching the pharmacological basis and mechanisms of Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM). He is internationally recognized for pioneering the theory of serum pharmacochemistry of TCM and the methodology of TCM formula and syndrome metabonomics. He has developed an innovative technical system for modern TCM research.

Jules A. Hoffman (French)
Nobel Prize laureate in Physiology or Medicine (2011)
Honorary Distinguished Research Director and Group Leader at the French National Center for Scientific Research (CNRS)
President of the French Academy of Sciences (2007-2008)
Hoffmann was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for his discoveries concerning the activation of innate immunity. He is renowned for his research on the genetic mechanisms and innate immune responses in insects, making him a globally recognized leader in the field of immunology.

Clemens Kaminski (British)
Head of the Department of Chemical Engineering and Biotechnology at the University of Cambridge
Fellow of the Institute of Physics (2020)
Fellow of the Royal Society of Chemistry (2020)
Clemens Kaminski is an internationally renowned scientist in high-resolution imaging technology. He is a pioneer in integrating cutting-edge technologies, including modern molecular biology, high-resolution imaging, and deep learning technologies. His work is dedicated to the precise research and visualization of molecular and organelle mechanisms.

Jean-Luc IMLER (French)
Director of the Institute of Molecular and Cellular Biology at the French National Center for Scientific Research (CNRS)
Director of the laboratory Insect Models of Innate Immunity Research Unit at CNRS
Recipient of the CNRS Silver Medal (2020)
Jean-Luc Imler is a leading figure in the study of antiviral immunity in flies. He has long been engaged in research on the antiviral mechanisms of RNA interference (RNAi), inducible antiviral immunity, and the identification of host factors that regulate viral infections. His team was the first to reveal the RNA immunity mechanism against viral infections.

Zhang Yongmin (French)
Fellow of the French National Academy of Pharmacy (2012)
First-Class Research Director at the French National Center for Scientific Research (CNRS) (2013)
PhD Supervisor at the Sorbonne University (formerly Pierre and Marie Curie University)
Zhang Yongmin is a leading expert in the study of bioactive carbohydrates. He has made significant contributions to carbohydrate chemistry and polysaccharide research, excelling in the study of the dose-effect, spectrum-effect, and structure-effect relationships of complex polysaccharides, achieving international recognition.

David M. Eisenberg (American)
Associate Professor at the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health
Founding Director of the Division for Research and Education in Complementary and Integrative Medical Therapies at Harvard Medical School (2000-2010)
Former Advisor to the National Institutes of Health (NIH), Food and Drug Administration (FDA), and the Federation of State Medical Boards
Eisenberg was the first American medical exchange student sent to China by the National Academy of Sciences in 1979. He specializes in the modern scientific validation of Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) and research on nutrition and disease prevention strategies, including lifestyle interventions. He offers unique insights into the contemporary medical interpretation of TCM wellness practices.

Wang Qi (Chinese)
Fellow of the Chinese Academy of Engineering (2019)
Certified National Chinese Medicine Master in the Second Guo Yi Da Shi selection
Lifetime Professor (First-Class Professor) at Beijing University of Chinese Medicine
Wang Qi discovered and defined nine types of Chinese body constitution. He initiated the Medical Health China Program of Nine Body Constitutions, then has developed and refined six major academic systems in Traditional Chinese Medicine: body constitution, male health, Zangxiang (phenomenon of organs), abdominal diagnosis, health medicine, and pre-disease medicine. His work has pioneered new areas of original thinking in Traditional Chinese Medicine.

Wang Xinlu (Chinese)
Certified National Chinese Medicine Master in the Fourth Guo Yi Da Shi selection
Chief Health Science Popularization Expert at the Chinese Association of Chinese Medicine
Professor and PhD Supervisor at Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine
Wang Xinlu is a leading researcher in the study of blood stasis theory. Having long been engaged in theoretical research and clinical practice in Traditional Chinese Medicine, he has established a solid theoretical foundation, extensive professional knowledge, and sufficient clinical experience.

Du Zhiyun (Chinese)
Provincial Talent of the "Thousand-Hundred-Ten" Program in Guangdong Province
Foreign Member of the Russian Academy of Natural Sciences
Chairman of the Guangdong Cosmetics Association
Du Zhiyun specializes in utilizing natural medicines and Chinese herbs, with a focus on the dual-purpose application of food as medicine. Employing systems biology and experimental pharmacology, he dedicates his research to developing new drugs, medical translational applications, functional foods, and functional cosmetics. His work emphasizes fundamental research and the industrial transformation within the health industry.

Robert Kam Ming KO (Hong Kong, China)
Associate Head and Professor, Division of Life Science, Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST)
Associate Director of Center for Chinese Medicine Research and Development
Robert Kam Ming Ko specializes in the pharmacological mechanisms of Traditional Chinese Medicines and formulae. He is particularly skilled in researching the components of Schisandra Chinensis, an invigorating Chinese herb, and its mechanisms for free radical scavenging, antioxidation, and anti-aging.

Wang Xijun (Chinese)
Director of the Research Center for Classic Formulae of the Ministry of Education
Director of the Metabolomics Research Center for Chinese Herbal Formulae at the National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine
Advocate of the Key Discipline A+ in Traditional Chinese Medicine
Wang Xijun has dedicated himself to researching the pharmacological basis and mechanisms of Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM). He is internationally recognized for pioneering the theory of serum pharmacochemistry of TCM and the methodology of TCM formula and syndrome metabonomics. He has developed an innovative technical system for modern TCM research.
Hoffmann-Infinitus Program
In March 2017, Professor Jules A. Hoffmann, the 2011 Nobel Prize laureate in Physiology or Medicine, was appointed as the Scientific Advisor to Infinitus, initiating long-term research on Chinese medicinal herbs. Later that year, in October, the "Hoffmann-Infinitus Research Program" was officially established in collaboration with the French National Center for Scientific Research (CNRS), Europe’s largest basic science research institution. This program supports Professor Hoffmann and his team in conducting scientific research aimed at enhancing product efficacy and advancing the understanding of the aging process. The research focuses on the antiviral and immunomodulatory effects of polysaccharides from Chinese herbs, improving gut immunity, and developing anti-aging formulations. These findings will be used to substantiate and elaborate the scientific basis of Infinitus products, and aid in the development of new products.
Hoffmann-Infinitus Program
In March 2017, Professor Jules A. Hoffmann, the 2011 Nobel Prize laureate in Physiology or Medicine, was appointed as the Scientific Advisor to Infinitus, initiating long-term research on Chinese medicinal herbs. Later that year, in October, the "Hoffmann-Infinitus Research Program" was officially established in collaboration with the French National Center for Scientific Research (CNRS), Europe’s largest basic science research institution. This program supports Professor Hoffmann and his team in conducting scientific research aimed at enhancing product efficacy and advancing the understanding of the aging process. The research focuses on the antiviral and immunomodulatory effects of polysaccharides from Chinese herbs, improving gut immunity, and developing anti-aging formulations. These findings will be used to substantiate and elaborate the scientific basis of Infinitus products, and aid in the development of new products.
Hoffmann-Infinitus Program
In March 2017, Professor Jules A. Hoffmann, the 2011 Nobel Prize laureate in Physiology or Medicine, was appointed as the Scientific Advisor to Infinitus, initiating long-term research on Chinese medicinal herbs. Later that year, in October, the "Hoffmann-Infinitus Research Program" was officially established in collaboration with the French National Center for Scientific Research (CNRS), Europe’s largest basic science research institution. This program supports Professor Hoffmann and his team in conducting scientific research aimed at enhancing product efficacy and advancing the understanding of the aging process. The research focuses on the antiviral and immunomodulatory effects of polysaccharides from Chinese herbs, improving gut immunity, and developing anti-aging formulations. These findings will be used to substantiate and elaborate the scientific basis of Infinitus products, and aid in the development of new products.
Cambridge Infinitus Research Centre
Established in 2015, the Cambridge Infinitus Research Centre (CIRCE) is Infinitus’ first overseas scientific collaboration platform. Since its inception, CIRCE has been dedicated to utilizing advanced technologies, such as molecular biology, to study the active ingredients and mechanisms of Chinese herbal medicines. In the future, Infinitus will further strengthen its research collaboration with the University of Cambridge, focusing on anti-aging and accelerating the application of research findings. We are committed to providing high-quality health products to the public, helping more people achieve health, beauty, and happiness.
Cambridge Infinitus Research Centre
Established in 2015, the Cambridge Infinitus Research Centre (CIRCE) is Infinitus’ first overseas scientific collaboration platform. Since its inception, CIRCE has been dedicated to utilizing advanced technologies, such as molecular biology, to study the active ingredients and mechanisms of Chinese herbal medicines. In the future, Infinitus will further strengthen its research collaboration with the University of Cambridge, focusing on anti-aging and accelerating the application of research findings. We are committed to providing high-quality health products to the public, helping more people achieve health, beauty, and happiness.
Cambridge Infinitus Research Centre
Established in 2015, the Cambridge Infinitus Research Centre (CIRCE) is Infinitus’ first overseas scientific collaboration platform. Since its inception, CIRCE has been dedicated to utilizing advanced technologies, such as molecular biology, to study the active ingredients and mechanisms of Chinese herbal medicines. In the future, Infinitus will further strengthen its research collaboration with the University of Cambridge, focusing on anti-aging and accelerating the application of research findings. We are committed to providing high-quality health products to the public, helping more people achieve health, beauty, and happiness.

Professor Clemens Kaminski
Clemens Kaminski, a British national, is a Professor at the University of Cambridge and the Chief Scientist at the Cambridge Infinitus Research Centre (CIRCE). He also serves as the Head of the Department of Chemical Engineering and Biotechnology at the University of Cambridge. Professor Kaminski leads the collaboration between Infinitus and the University of Cambridge, focusing on elucidating the mechanisms of action of natural products and ingredients to develop products that maintain health and prevent diseases.
Professor Clemens Kaminski
Clemens Kaminski, a British national, is a Professor at the University of Cambridge and the Chief Scientist at the Cambridge Infinitus Research Centre (CIRCE). He also serves as the Head of the Department of Chemical Engineering and Biotechnology at the University of Cambridge. Professor Kaminski leads the collaboration between Infinitus and the University of Cambridge, focusing on elucidating the mechanisms of action of natural products and ingredients to develop products that maintain health and prevent diseases.
Professor Clemens Kaminski
Clemens Kaminski, a British national, is a Professor at the University of Cambridge and the Chief Scientist at the Cambridge Infinitus Research Centre (CIRCE). He also serves as the Head of the Department of Chemical Engineering and Biotechnology at the University of Cambridge. Professor Kaminski leads the collaboration between Infinitus and the University of Cambridge, focusing on elucidating the mechanisms of action of natural products and ingredients to develop products that maintain health and prevent diseases.

As of August 10, 2023, Infinitus holds a total of 651 patents, comprising 290 invention patents, 196 utility model patents, and 165 design patents.
0
有权专利(件)
0
发明专利(件)
0
设计专利(件)
0
实用新型专利(件)
As of August 10, 2023, Infinitus holds a total of 651 patents, comprising 290 invention patents, 196 utility model patents, and 165 design patents.
0
Valid patents (number of patents)
0
Invention patents (number of patents)
0
Design patents (number of patents)
0
Utility model patents (number of patents)
Academic Papers Published in International Journals
Academic Papers Published in International Journals
Regulation effects of indigestible dietary polysaccharides on intestinal microflora: An overview
Journal of Food Biochemistry
2020:el3564
Comparison of immunomodulatory effects of three polysaccharide fractions from Lentinula edodes water extracts
Journal of Functional Foods
2020,66:103791
Ultrahigh pressure extraction of polysaccharide from Morinda officinalis and effect on the polysaccharide structure
Separation Science and Technology
2020: 1-11
Photoprotective effect of Astragalus membranaceus polysaccharide on UVA-induced damage in HaCaT cells
Pios one
2020, 15(7): e0235515
Purification of polysaccharide from Lentinus edodes water extract by membrane separation and its chemical cosposition and structure character!zat ion
Food Hydrocolloids
3784:11:00.000
MPSSS impairs the immunosuppressive function of cancer-associated fibroblasts via the TLR4-NF- x B pathway MPSSS通过TLR4-NF-x B
Bioscience reports
2019, 39(5).
Purification of polysaccharide from Lentinus edodes water extract by membrane separation and its chemical cosposition and structure character!zat ion
Food & function
3784:11:00
MPSSS impairs the immunosuppressive function of cancer-associated fibroblasts via the TLR4-NF- x B pathway MPSSS通过TLR4-NF-x B
Bioscience reports
2019, 39(5).
Supplementation with compound polysaccharides contributes to the development and metabolic activity of young rat intestinal iaicrobiota 补充复合多糖有助于幼鼠肠道的发育和代谢活性
Food & function
2019, 10(5): 2658-2675
Study on quality regionalization of Lycii Fructus
China journal of Chinese materia medica
2019,44(6): 1156-1163.
Hematopoietic effect of small molecular fraction of Polygoni mult iflori Radix Praeparata in cyclophosphamide-induced anemia mice
Chinese journal of natural medicines
2019, 17(7): 535-544.
Comparison of Immunomodulatory Effects of Fresh Garlic and Black Garlic Polysaccharides on RAW 264. 7 Macrophages
Journal of Food Science,
2017, 82(3):765-771.
Purification, structural characterization, and immunomodulatory activity of the polysaccharides from Ganoderma lucidum
International Journal of Biological Macromolecules
2019
Lycium barbarum polysaccharides extend the mean lifespan of Drosophila melanogaster
Food & Function
2019, 10(7): 4231-4241
Alkaline Extraction, Structural Characterization, and Bioactivities of (l-*6)-p -d-Glucan from Lentinus edodes
Molecules
2019,24(8): 1610.
MPSSS impairs the immunosuppressive function of cancer-associated fibroblasts via the TLR4-NF- k B pathway MPSSS通过TLR4-NF- k B
Bioscience reports
2019, 39(5).
Comparison of structural, antioxidant and immuno - stimulating activities of polysaccharides from Tremella fuciformis in two different regions of China
International Journal of Food Science & Technology
201&53(8)
Polysaccharides from Chinese Herbal Lycium barbarum Induced Systemic and Local Immune Responses in H22 Tumor-Bearing Mice
Immunology Research
2018, Article ID 3431782,12 pages.
Fraction From Lycium barbarum Polysaccharides Reduces Inununotoxicity and Enhances Antitumor Activity of Doxorubicin in Mice.
Integrative Cancer Therapies
2018:15347354 1775354
Eugenol triggers CDllb+Grl+ myeloid-derived suppressor cell apoptosis via endogenous apoptosis pathway
Rsc Advances
2018, 8(7):3833-383&
An Asparagus polysaccharide fraction inhibits MDSCs by inducing apoptosis through toll-like receptor
Phytotherapy Research
2018(Suppl 2).
Effects of l.ycium barbarum polysaccharides with different molecular weights on function of RAW264. 7 macrophages
Food & Agricultural Immunology
2018:1-13
Effect of compound polysaccharide with Lentinan, Pachymaran and Tremella polysaccharide on mouse macrophage function
Chinese Journal of Immunology
2018
Myeloid-derived suppressor cells promote B-cell production of IgA in a TNPR2-dependent manner
Cellular & Molecular Immunology
2017, 14(7):597-606.
Immunoenhancenient of Edible Fungal Polysaccharides (Lentinan, Tremellan, and Pachymaran) on Cyclophosphamide-Induced Inununosuppression in Mouse Model
Evidence-based complementary and alternative medicine
2017, 2017(1):94591 56.
A polysaccharide from Dictyophora indusiata inhibits the immunosuppressive function of cancer -associated fibroblasts
Cell Biochemistry & Function
2017,35(7).
Effect of edible fungal polysaccharides on improving influenza vaccine protection in mice
Food & Agricultural Immunology
2017, 28(6): 1- 12.
A polysaccharide derived from Lentinus edodes impairs the immunosuppressive function of myeloid-derived suppressor cells via the p38 pathways
Rsc Advances
2017, 7(58)
Effect of polysaccharides from Tremella fuciformis, on UV-induced photoaging
Journal of Functional Foods
2016,20:400- 410.
Inununofflodulatory effects of polysaccharide cexpounds in macrophages revealed by high resolution ATM
Scanning
2016, 38(6)
Polysaccharides from medicinal herbs as potential therapeutics for aging and age-related neurodegeneration
Rejuvenation research
2014,17(2): 201-204.
Optimization for the extraction of polysaccharides from Ganoderma lucidum, and their antioxidant and antiproliferative activities
Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers
2013, 44(6):886-894
Polysaccharide from Lentinus edodes inhibits the immunosuppressive function of myeloid-derived suppressor cells
PloS one
2012,7(12): e51751.
Long-Term Treatment with a Compound Polysaccharide-Based Health Product (Infinitus Polysac Plus) Enhances Innate and Adaptive Immunity in Mice
Chinese Medicine
2011,2(04): 178.
Extraction and Antioxidant Activity of a Combined Fungus Polysaccharide
Journal of Food Science and Biotechnology
2013,3.
A homogalacturonan from the radix of Platycodon grandiflorum, and the anti-angiogenesis activity of po1y-/o1igoga1acturonic acids derived therefrom
Carbohydrate Research
2011, 346(13):1930-6
Comparison of Methods for Determination of Polysaccharides Content in Epiphyte Health Foods
Modern Food Science and Technology
2010,7.
Polysaccharides in Lentinus edodes: Isolation, Structure, Immunomodulating Activity and Future Prospective
Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition
54:474487 (2014)
Modulation of Gut Microbiome Composition and Function in Experimental Colitis Treated with Sulfasalazine
Frontiers in Microbiology
2017, 8 (9) : 1-15
Regulation effects of indigestible dietary polysaccharides on intestinal microflora: An overview
Journal of Food Biochemistry
2020:el3564
Comparison of immunomodulatory effects of three polysaccharide fractions from Lentinula edodes water extracts
Journal of Functional Foods
2020,66:103791
Ultrahigh pressure extraction of polysaccharide from Morinda officinalis and effect on the polysaccharide structure
Separation Science and Technology
2020: 1-11
Photoprotective effect of Astragalus membranaceus polysaccharide on UVA-induced damage in HaCaT cells
Pharmacology & Pharmacy
2019, 10(6):318-328
Purification of polysaccharide from Lentinus edodes water extract by membrane separation and its chemical cosposition and structure character!zat ion
Food Hydrocolloids
3784:11:00.000
MPSSS impairs the immunosuppressive function of cancer-associated fibroblasts via the TLR4-NF- x B pathway MPSSS
Bioscience reports
2019, 39(5).
Purification of polysaccharide from Lentinus edodes water extract by membrane separation and its chemical cosposition and structure character!zat ion
Food & function
3784:11:00
MPSSS impairs the immunosuppressive function of cancer-associated fibroblasts via the TLR4-NF- x B pathway MPSSS通过TLR4-NF-x B
Bioscience reports
2019, 39(5).
Supplementation with compound polysaccharides contributes to the development and metabolic activity of young rat intestinal iaicrobiota
Food & function
2019, 10(5): 2658-2675
Study on quality regionalization of Lycii Fructus
China journal of Chinese materia medica
2019,44(6): 1156-1163.
Hematopoietic effect of small molecular fraction of Polygoni mult iflori Radix Praeparata in cyclophosphamide-induced anemia mice
Chinese journal of natural medicines
2019, 17(7): 535-544.
Comparison of Immunomodulatory Effects of Fresh Garlic and Black Garlic Polysaccharides on RAW 264. 7 Macrophages
Journal of Food Science,
2017, 82(3):765-771.
Purification, structural characterization, and immunomodulatory activity of the polysaccharides from Ganoderma lucidum
International Journal of Biological Macromolecules
2019
Lycium barbarum polysaccharides extend the mean lifespan of Drosophila melanogaster
Food & Function
2019, 10(7): 4231-4241
Alkaline Extraction, Structural Characterization, and Bioactivities of (l-*6)-p -d-Glucan from Lentinus edodes
Molecules
2019,24(8): 1610.
MPSSS impairs the immunosuppressive function of cancer-associated fibroblasts via the TLR4-NF- k B pathway MPSSS通过TLR4-NF- k B
Bioscience reports
2019, 39(5).
Comparison of structural, antioxidant and immuno - stimulating activities of polysaccharides from Tremella fuciformis in two different regions of China
International Journal of Food Science & Technology
201&53(8)
Polysaccharides from Chinese Herbal Lycium barbarum Induced Systemic and Local Immune Responses in H22 Tumor-Bearing Mice
Immunology Research
2018, Article ID 3431782,12 pages.
Fraction From Lycium barbarum Polysaccharides Reduces Inununotoxicity and Enhances Antitumor Activity of Doxorubicin in Mice.
Integrative Cancer Therapies
2018:15347354 1775354
Eugenol triggers CDllb+Grl+ myeloid-derived suppressor cell apoptosis via endogenous apoptosis pathway
Rsc Advances
2018, 8(7):3833-383&
An Asparagus polysaccharide fraction inhibits MDSCs by inducing apoptosis through toll-like receptor
Phytotherapy Research
2018(Suppl 2).
Effects of l.ycium barbarum polysaccharides with different molecular weights on function of RAW264. 7 macrophages
Food & Agricultural Immunology
2018:1-13
Effect of compound polysaccharide with Lentinan, Pachymaran and Tremella polysaccharide on mouse macrophage function
Chinese Journal of Immunology
2018
Myeloid-derived suppressor cells promote B-cell production of IgA in a TNPR2-dependent manner
Cellular & Molecular Immunology
2017, 14(7):597-606.
Immunoenhancenient of Edible Fungal Polysaccharides (Lentinan, Tremellan, and Pachymaran) on Cyclophosphamide-Induced Inununosuppression in Mouse Model
Evidence-based complementary and alternative medicine
2017, 2017(1):94591 56.
A polysaccharide from Dictyophora indusiata inhibits the immunosuppressive function of cancer -associated fibroblasts
Cell Biochemistry & Function
2017,35(7).
Effect of edible fungal polysaccharides on improving influenza vaccine protection in mice
Food & Agricultural Immunology
2017, 28(6): 1- 12.
A polysaccharide derived from Lentinus edodes impairs the immunosuppressive function of myeloid-derived suppressor cells via the p38 pathways
Rsc Advances
2017, 7(58)
Effect of polysaccharides from Tremella fuciformis, on UV-induced photoaging
Journal of Functional Foods
2016,20:400- 410.
Inununofflodulatory effects of polysaccharide cexpounds in macrophages revealed by high resolution ATM
Scanning
2016, 38(6)
Polysaccharides from medicinal herbs as potential therapeutics for aging and age-related neurodegeneration
Rejuvenation research
2014,17(2): 201-204.
Optimization for the extraction of polysaccharides from Ganoderma lucidum, and their antioxidant and antiproliferative activities
Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers
2013, 44(6):886-894
Polysaccharide from Lentinus edodes inhibits the immunosuppressive function of myeloid-derived suppressor cells
PloS one
2012,7(12): e51751.
Long-Term Treatment with a Compound Polysaccharide-Based Health Product (Infinitus Polysac Plus) Enhances Innate and Adaptive Immunity in Mice
Chinese Medicine
2011,2(04): 178.
Extraction and Antioxidant Activity of a Combined Fungus Polysaccharide
Journal of Food Science and Biotechnology
2013,3.
A homogalacturonan from the radix of Platycodon grandiflorum, and the anti-angiogenesis activity of po1y-/o1igoga1acturonic acids derived therefrom
Carbohydrate Research
2011, 346(13):1930-6
Comparison of Methods for Determination of Polysaccharides Content in Epiphyte Health Foods
Modern Food Science and Technology
2010,7.
Polysaccharides in Lentinus edodes: Isolation, Structure, Immunomodulating Activity and Future Prospective
Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition
54:474487 (2014)
Modulation of Gut Microbiome Composition and Function in Experimental Colitis Treated with Sulfasalazine
Frontiers in Microbiology
2017, 8 (9) : 1-15
Regulation effects of indigestible dietary polysaccharides on intestinal microflora: An overview
Journal of Food Biochemistry
2020:el3564
Comparison of immunomodulatory effects of three polysaccharide fractions from Lentinula edodes water extracts
Journal of Functional Foods
2020,66:103791
Ultrahigh pressure extraction of polysaccharide from Morinda officinalis and effect on the polysaccharide structure
Separation Science and Technology
2020: 1-11
Photoprotective effect of Astragalus membranaceus polysaccharide on UVA-induced damage in HaCaT cells
Pios one
2020, 15(7): e0235515
Purification of polysaccharide from Lentinus edodes water extract by membrane separation and its chemical cosposition and structure character!zat ion
Food Hydrocolloids
3784:11:00.000
MPSSS impairs the immunosuppressive function of cancer-associated fibroblasts via the TLR4-NF- x B pathway MPSSS
Bioscience reports
2019, 39(5).
Purification of polysaccharide from Lentinus edodes water extract by membrane separation and its chemical cosposition and structure character!zat ion
Food & function
3784:11:00
MPSSS impairs the immunosuppressive function of cancer-associated fibroblasts via the TLR4-NF- x B pathway MPSSS
Bioscience reports
2019, 39(5).
Supplementation with compound polysaccharides contributes to the development and metabolic activity of young rat intestinal iaicrobiota
Food & function
2019, 10(5): 2658-2675
Study on quality regionalization of Lycii Fructus
China journal of Chinese materia medica
2019,44(6): 1156-1163.
Hematopoietic effect of small molecular fraction of Polygoni mult iflori Radix Praeparata in cyclophosphamide-induced anemia mice
Chinese journal of natural medicines
2019, 17(7): 535-544.
Comparison of Immunomodulatory Effects of Fresh Garlic and Black Garlic Polysaccharides on RAW 264. 7 Macrophages
Journal of Food Science,
2017, 82(3):765-771.
Purification, structural characterization, and immunomodulatory activity of the polysaccharides from Ganoderma lucidum
International Journal of Biological Macromolecules
2019
Lycium barbarum polysaccharides extend the mean lifespan of Drosophila melanogaster
Food & Function
2019, 10(7): 4231-4241
Alkaline Extraction, Structural Characterization, and Bioactivities of (l-*6)-p -d-Glucan from Lentinus edodes
Molecules
2019,24(8): 1610.
MPSSS impairs the immunosuppressive function of cancer-associated fibroblasts via the TLR4-NF- k B pathway MPSSS
Bioscience reports
2019, 39(5).
Comparison of structural, antioxidant and immuno - stimulating activities of polysaccharides from Tremella fuciformis in two different regions of China
International Journal of Food Science & Technology
201&53(8)
Polysaccharides from Chinese Herbal Lycium barbarum Induced Systemic and Local Immune Responses in H22 Tumor-Bearing Mice
Immunology Research
2018, Article ID 3431782,12 pages.
Fraction From Lycium barbarum Polysaccharides Reduces Inununotoxicity and Enhances Antitumor Activity of Doxorubicin in Mice.
Integrative Cancer Therapies
2018:15347354 1775354
Eugenol triggers CDllb+Grl+ myeloid-derived suppressor cell apoptosis via endogenous apoptosis pathway
Rsc Advances
2018, 8(7):3833-383&
An Asparagus polysaccharide fraction inhibits MDSCs by inducing apoptosis through toll-like receptor
Phytotherapy Research
2018(Suppl 2).
Effects of l.ycium barbarum polysaccharides with different molecular weights on function of RAW264. 7 macrophages
Food & Agricultural Immunology
2018:1-13
Effect of compound polysaccharide with Lentinan, Pachymaran and Tremella polysaccharide on mouse macrophage function
Chinese Journal of Immunology
2018
Myeloid-derived suppressor cells promote B-cell production of IgA in a TNPR2-dependent manner
Cellular & Molecular Immunology
2017, 14(7):597-606.
Immunoenhancenient of Edible Fungal Polysaccharides (Lentinan, Tremellan, and Pachymaran) on Cyclophosphamide-Induced Inununosuppression in Mouse Model
Evidence-based complementary and alternative medicine
2017, 2017(1):94591 56.
A polysaccharide from Dictyophora indusiata inhibits the immunosuppressive function of cancer -associated fibroblasts
Cell Biochemistry & Function
2017,35(7).
Effect of edible fungal polysaccharides on improving influenza vaccine protection in mice
Food & Agricultural Immunology
2017, 28(6): 1- 12.
A polysaccharide derived from Lentinus edodes impairs the immunosuppressive function of myeloid-derived suppressor cells via the p38 pathways
Rsc Advances
2017, 7(58)
Effect of polysaccharides from Tremella fuciformis, on UV-induced photoaging
Journal of Functional Foods
2016,20:400- 410.
Inununofflodulatory effects of polysaccharide cexpounds in macrophages revealed by high resolution ATM
Scanning
2016, 38(6)
Polysaccharides from medicinal herbs as potential therapeutics for aging and age-related neurodegeneration
Rejuvenation research
2014,17(2): 201-204.
Optimization for the extraction of polysaccharides from Ganoderma lucidum, and their antioxidant and antiproliferative activities
Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers
2013, 44(6):886-894
Polysaccharide from Lentinus edodes inhibits the immunosuppressive function of myeloid-derived suppressor cells
PloS one
2012,7(12): e51751.
Long-Term Treatment with a Compound Polysaccharide-Based Health Product (Infinitus Polysac Plus) Enhances Innate and Adaptive Immunity in Mice
Chinese Medicine
2011,2(04): 178.
Extraction and Antioxidant Activity of a Combined Fungus Polysaccharide
Journal of Food Science and Biotechnology
2013,3.
A homogalacturonan from the radix of Platycodon grandiflorum, and the anti-angiogenesis activity of po1y-/o1igoga1acturonic acids derived therefrom
Carbohydrate Research
2011, 346(13):1930-6
Comparison of Methods for Determination of Polysaccharides Content in Epiphyte Health Foods
Modern Food Science and Technology
2010,7.
Polysaccharides in Lentinus edodes: Isolation, Structure, Immunomodulating Activity and Future Prospective
Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition
54:474487 (2014)
Modulation of Gut Microbiome Composition and Function in Experimental Colitis Treated with Sulfasalazine
Frontiers in Microbiology
2017, 8 (9) : 1-15
Headquarters and Laboratory Resources
Headquarters and Laboratory Resources
Infinitus Plaza - The Global Headquarters
Infinitus Plaza, located on Des Voeux Road Central in Sheung Wan, is a renowned stylish landmark in Hong Kong. The new Infinitus Plaza in Guangzhou, inaugurated in November 2021, represents Infinitus' dedication to excellence, blending fashion, environmental sustainability, and technology altogether. Designed by the "Queen of International Architecture," Zaha Hadid, the plaza's "∞" layout embodies the "Infinitus" philosophy, integrating high-tech elements to create a new and stylish landmark of health and wellness in Guangzhou.
Developed over five years with a total investment of RMB 4.5 billion, the plaza spans approximately 45,000 square meters, with a total construction area of 185,000 square meters. Guangzhou Infinitus Plaza is comprised of the Infinitus Global Executive Headquarters, Global Research Center, and Global Customer Experience Center, merging ecological sustainability, health, fashion, and technological intelligence.
The plaza features over 60 professional laboratories dedicated to researching health food technology, clean chemical household products, and health and wellness products, as well as conducting product inspections. The research center emphasizes the core technology, efficacy, and safety of herbal health products, aiming to standardize and internationalize traditional Chinese herbal products.
Production
Smart Green Production Bases
To provide consumers with green, healthy, and high-quality products, Infinitus continuously upgrades its production processes, creating environmentally friendly, high-tech smart factories. The company has established two major production bases in mainland China: Xinhui and Yingkou. Infinitus pioneered China's first high-speed glass bottle production line for the oral tonic that meets health food GMP standards, strictly adhering to national GMP standards for production and quality management.
Infinitus Production Base in Xinhui
Located in Xinhui, Jiangmen, Guangdong Province, the Infinitus Xinhui Production Base's first phase was completed and put into operation on February 26, 2005. The second and third phases were completed and began operations between 2008 and 2012, with a total investment exceeding RMB13 billion. Covering approximately 200,000 square meters, the base serves as an immersive experience space for showcasing, experiencing, and exchanging ideas. It has become a platform for displaying Infinitus' corporate culture and product experiences.
Infinitus Yingkou Production Base
Situated in Yingkou, Liaoning Province, this production base covers about 350,000 square meters. It includes production buildings, an inspection center, exhibition halls, and specially designed visitor viewing panels, making it a multifunctional platform for corporate culture display and product experiences. The base comprises premises for extraction, oral tonic production, solid product preparation, inspection center, office building, restaurant, staff dormitories, and utility engineering. All are of low energy consumption, low emissions, and high efficiency.
Infinitus Product Inspection Center
The product inspection centers at Infinitus production bases have received consecutive accreditations from laboratories certified by the China National Accreditation Service for Conformity Assessment (CNAS), UK FAPAS (for heavy metals and pesticide residue testing), German DRRR (for nutritional content testing), and UK LGC (for international proficiency testing). This recognition from multiple internationally renowned institutions underscores Infinitus' commitment to enhancing testing capabilities, ensuring quality, and providing safer, higher-quality products.
Raw Ingredient Cultivation
Authentic Raw Ingredients
For 31 years, Infinitus has considered quality its cornerstone in the health and wellness industry. By establishing a comprehensive raw ingredient management model that covers the entire industry chain, Infinitus ensures product quality and safety at every stage, from raw ingredient cultivation and product R&D to production, logistics, and after-sales services. Infinitus enforces stringent safety requirements for raw ingredients, conducting 180 pesticide residue scans and five heavy metal tests to ensure all ingredients meet green standards. The company adopts rigorous standards for selecting origins and growers for the raw ingredients, treating fields as the extension of our factories. Through the comprehensive management and monitoring of the entire process—from germplasm, ecological environment, and field management to harvesting, processing, storage, and logistics—Infinitus guarantees high-quality, effective, and genuinely authentic raw ingredients.

Five Standardizations
1. Standardized Species: Take Ganoderma Sinensis (Lingzhi) for example, Infinitus exclusively selects authentic Ganoderma lucidum (Lingzhi) seedlings from Longquan, Zhejiang. The best seedlings are chosen to achieve comprehensive efficacy, strong resistance to pests and diseases, and optimial productivity.
2. Standardized Production Specifications - Standardized procurement protocol reduces the risk of non-compliance.
3. Standardized Field Management - Planting techniques and management standards are developed based on the growth characteristics and environmental requirements of each raw ingredient.
4. Standardized Technical Support - Experts are invited annually to provide professional guidance to growers.
5. Standardized Harvesting and Processing – Infinitus strictly manages farmers according to the planting and harvesting standards for authentic medicinal ingredients to ensure the best quality. Improper harvesting times can affect the quality of raw ingredients. Therefore, Infinitus meticulously follows the growth cycle of each ingredient. For instance, Poria Cocos takes three years of growth before it can be harvested. We strictly follow its life cycle to ensure its optimal quality.
Product quality is the cornerstone of a company's growth and its most significant promise to consumers. The cultivation and production of Chinese herbal medicines involve complex and sophisticated processes that demand exceptional growing conditions and advanced cultivation techniques. "The use of authentic raw ingredients" is not just a marketing gimmick. By actualizing it, not only a high-quality natural environment is required, but also exemplary planting and cultivation practices. In 2022, Infinitus, in collaboration with renowned microbiologist Academician Wu Qingping, developed an exclusive strain of Ganoderma Sinensis (Lingzhi).
Five Standardizations
1. Standardized Species: Take Ganoderma Sinensis (Lingzhi) for example, Infinitus exclusively selects authentic Ganoderma lucidum (Lingzhi) seedlings from Longquan, Zhejiang. The best seedlings are chosen to achieve comprehensive efficacy, strong resistance to pests and diseases, and optimial productivity.
2. Standardized Production Specifications - Standardized procurement protocol reduces the risk of non-compliance.
3. Standardized Field Management - Planting techniques and management standards are developed based on the growth characteristics and environmental requirements of each raw ingredient.
4. Standardized Technical Support - Experts are invited annually to provide professional guidance to growers.
5. Standardized Harvesting and Processing – Infinitus strictly manages farmers according to the planting and harvesting standards for authentic medicinal ingredients to ensure the best quality. Improper harvesting times can affect the quality of raw ingredients. Therefore, Infinitus meticulously follows the growth cycle of each ingredient. For instance, Poria Cocos takes three years of growth before it can be harvested. We strictly follow its life cycle to ensure its optimal quality.
Product quality is the cornerstone of a company's growth and its most significant promise to consumers. The cultivation and production of Chinese herbal medicines involve complex and sophisticated processes that demand exceptional growing conditions and advanced cultivation techniques. "The use of authentic raw ingredients" is not just a marketing gimmick. By actualizing it, not only a high-quality natural environment is required, but also exemplary planting and cultivation practices. In 2022, Infinitus, in collaboration with renowned microbiologist Academician Wu Qingping, developed an exclusive strain of Ganoderma Sinensis (Lingzhi).
Five Standardizations
1. Standardized Species: Take Ganoderma Sinensis (Lingzhi) for example, Infinitus exclusively selects authentic Ganoderma lucidum (Lingzhi) seedlings from Longquan, Zhejiang. The best seedlings are chosen to achieve comprehensive efficacy, strong resistance to pests and diseases, and optimial productivity.
2. Standardized Production Specifications - Standardized procurement protocol reduces the risk of non-compliance.
3. Standardized Field Management - Planting techniques and management standards are developed based on the growth characteristics and environmental requirements of each raw ingredient.
4. Standardized Technical Support - Experts are invited annually to provide professional guidance to growers.
5. Standardized Harvesting and Processing – Infinitus strictly manages farmers according to the planting and harvesting standards for authentic medicinal ingredients to ensure the best quality. Improper harvesting times can affect the quality of raw ingredients. Therefore, Infinitus meticulously follows the growth cycle of each ingredient. For instance, Poria Cocos takes three years of growth before it can be harvested. We strictly follow its life cycle to ensure its optimal quality.
Product quality is the cornerstone of a company's growth and its most significant promise to consumers. The cultivation and production of Chinese herbal medicines involve complex and sophisticated processes that demand exceptional growing conditions and advanced cultivation techniques. "The use of authentic raw ingredients" is not just a marketing gimmick. By actualizing it, not only a high-quality natural environment is required, but also exemplary planting and cultivation practices. In 2022, Infinitus, in collaboration with renowned microbiologist Academician Wu Qingping, developed an exclusive strain of Ganoderma Sinensis (Lingzhi).
Quality Inspection
Rigorous Quality Management from the Field All the Way till Reaching Consumers
For 31 years, Infinitus has viewed quality as its core focus. Through a comprehensive raw ingredient management system, the company ensures product quality and safety throughout every stage— from cultivation and research to production, logistics, and after-sales services.
100-1=0
Our quality control motto, "100-1 = 0," signifies our commitment to zero tolerance for errors. Every product undergoes rigorous testing—often thousands of tests—to ensure compliance with international quality and safety standards.

Safety Commitment
Infinitus has invested over USD400 million and USD220 million respectively in building two major production bases in Xinhui, Jiangmen, Guangdong Province, and Yingkou, Liaoning Province, covering an area of over 550,000 square meters. Xinhui Production Base holds ISO9001, FSSC22000, GMP, and HACCP certifications, while Yingkou Production Baes is certified with ISO9001, FSSC22000, and HACCP. Both production bases have been recognized by major international authorities such as ISO, FSSC, and HACCP.
Our safety commitment is also validated by FAPAS certification. FAPAS is a leading global provider of laboratory testing services, ensuring our inspection capabilities are of the highest standard.



























